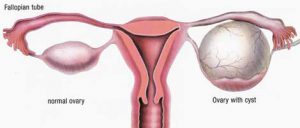
Ovarian cysts are fluid-filled sacs or pockets within or on the surface of an ovary. Women have two ovaries — each about the size and shape of an almond — located on each side of the uterus. Eggs (ova) develop and mature in the ovaries and are released in monthly cycles during your childbearing years. Many women have ovarian cysts at some time during their lives. Most ovarian cysts present little or no discomfort and are harmless. The majority of ovarian cysts disappear without treatment within a few months.
However, ovarian cysts — especially those that have ruptured — sometimes produce serious symptoms. The best ways to protect your health are to know the symptoms that may signal a more significant problem, and to schedule regular pelvic examinations.
Symptoms
Most cysts don’t cause any symptoms and go away on their own. A large ovarian cyst can cause abdominal discomfort. If a large cyst presses on your bladder, you may feel the need to urinate more frequently because bladder capacity is reduced.
The symptoms of ovarian cysts, if present, may include:
- Menstrual irregularities
- Pelvic pain a constant or intermittent dull ache that may radiate to your lower back and thighs
- Pelvic pain shortly before your period begins or just before it ends
- Pelvic pain during intercourse (dyspareunia)
- Pain during bowel movements or pressure on your bowels
- Nausea, vomiting or breast tenderness similar to that experienced during pregnancy
- Fullness or heaviness in your abdomen
- Pressure on your rectum or bladder that causes a need to urinate more frequently or difficulty emptying your bladder completely
